Beginner’s 101
What Does CBD do?

It can be confusing stuff if you’ve ever wanted to try CBD, but you’re not sure what it does. It’s important to note that while CBD is extremely popular, you should always do your own research to know the in’s and out’s before you begin.
Here we break down the facts to help you decide if CBD is right for you. With a wealth of anecdotal stories out there that tell of the vast array of benefits, you may be hard-pressed to find out what CBD doesn’t do rather than what it does.
To get a better understanding of what CBD does, we’ve put together this beginner’s guide to help you get to know the basics. In this article we’ll answer many of your questions about CBD.
What does CBD do?
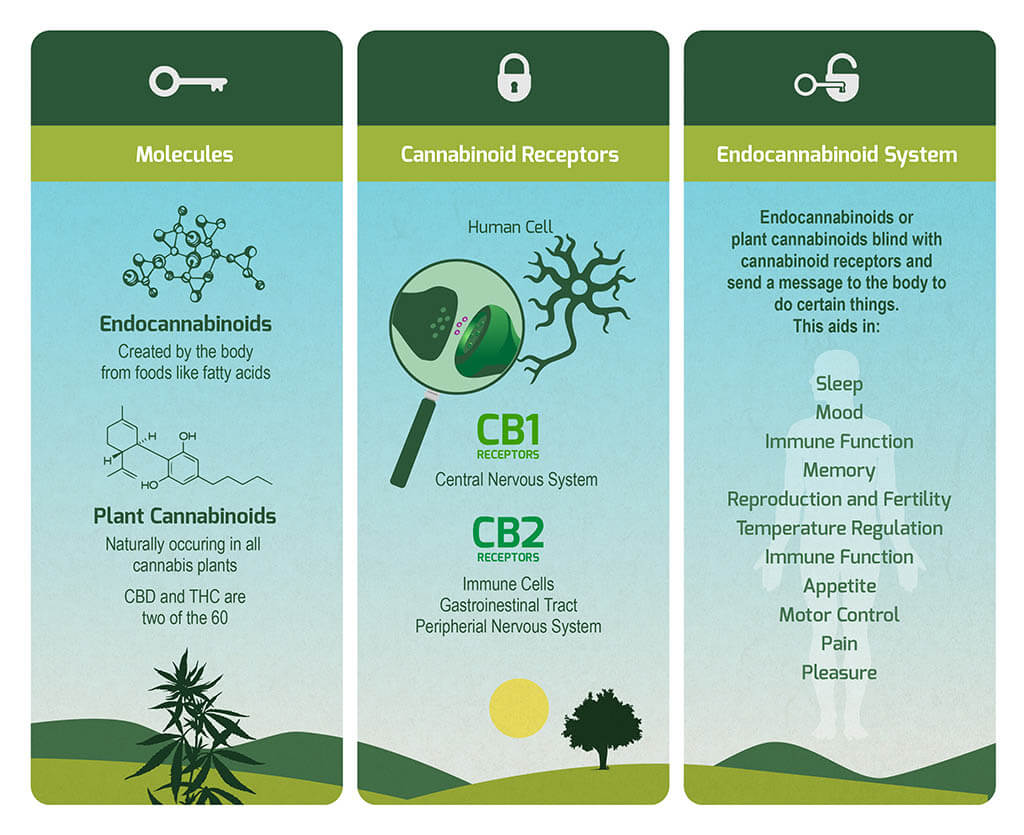
You may have heard of CBD, but what does it do exactly? how it interacts with your body helps to explain how it all works.
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a plant cannabinoid that is found in the cannabis plant. One of the main things CBD is able to do is to interact with neurotransmitters, which send messages to the cells in your body. By working with your endocannabinoid system, the molecule stimulates cell receptors to promote homeostasis, otherwise known as balance.
While the endocannabinoid system is one of the lesser-known bodily systems, it is responsible for regulating some of its most important functions, including sleep, immunity, mood, and pain response.
What do cannabinoids do? Cannabinoids are produced naturally by the body and are also found in plants called phytocannabinoids. When cannabinoids are introduced to the body they help to stimulate the endocannabinoid system to regulate balance.
There are two main receptors in the body that receive messages from cannabinoids. These are your CB1 and CB2. CBD is known to have a mild stimulating effect on the CB2, by helping it to create more of the body’s own endocannabinoids.
Similar to a ‘dimmer switch’, the endocannabinoid system regulates the body up or down when things seem out of balance. You will find this system in most of your vital organs, in the brain, central nervous system, reproductive and digestive system, controlling hormones and enzymes, that affect your sleep, mood, and pain responses.
Does CBD make you high?
Unlike THC, which binds to CB1 receptors, CBD has a low binding affinity to neurotransmitters and stimulates them to promote more endocannabinoids. Because CBD doesn’t attach itself to receptors it doesn’t have any of the high inducing effects.
The compound cannabidiol is found in both hemp and high THC cannabis strains, which can cause confusion about its effects. Hemp is a non-psychoactive version of cannabis, classified by its very low levels of THC, which are as low as 0.2-0.3%. CBD is one over 80 different types of cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant.
Hemp is often the main source of CBD because of its low THC content. CBD is not psychoactive and doesn’t cause a high, known only for its therapeutic qualities. It comes in a variety of forms from CBD oils to capsules and even CBD creams, depending on what you are looking for.
You may also like to read THC vs CBD to find out more about the differences.
Does CBD get you high?
Due to its non-psychoactive properties, CBD feels very different from its counterpart THC, it doesn’t get you high. Some users report feelings of calm, focus, or deep relaxation, without any of the euphoria or mind-altering effects traditionally connected to cannabis.
The way CBD feels can be extremely varied amongst users, so how it affects one person may not be the same for another. It all depends on your individual endocannabinoid system and how it reacts to cannabinoids.
What is CBD used for?
While CBD is popular with users for a wide variety of ailments. There is still limited scientific evidence on its effects on specific conditions. As far as medical research goes, there isn’t enough evidence to say what CBD is good for definitively.
CBD is still in the early stages of being recognized as a viable medical treatment, therefore until more research is conducted, users rely heavily on anecdotal evidence to find out what it can be used for.
Currently, CBD has not been approved by The Food and Drug Administration (FDA), therefore brands must follow guidelines regarding non-approved products if they are marketing them to the public.
Epidiolex is the only form of CBD that is approved by the FDA, an epileptic pharmaceutical drug used for the treatment of rare forms of childhood epilepsy called Draventport and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. This treatment is used to reduce seizures and is only available on prescription.
Are there different types of CBD?
You may have heard of terms like full-spectrum, isolate, or broad-spectrum and wondered does this make any difference? These terms relate to product formulas, which can affect the way CBD works.
CBD is compound therefore it stays the same. However, the formula in which it comes can vary and it does have an impact on its effects. Through a process called the ‘entourage effect’, where each cannabinoid works in synergy to create an amplified effect.
What does Full Spectrum mean?
Full-spectrum is where the cannabinoids found in the natural hemp plant, still remain present. This formula is as close to the real plant as you can get. Hemp has over 80 different types of cannabinoids, that all work in unison to increase CBD’s effects.
As this version of CBD is derived from hemp, it still contains a small amount of THC at 0.2-0.3%. As well as other beneficial plant components, such as terpenes, flavonoids, and waxes. Including omegas 3, 6 & 9, vitamin E, and other essential vitamins.
What does Isolate CBD mean?
A 99% pure CBD crystalline or powder formula that has been extracted and isolated from all plant materials and other cannabinoids, including THC. This is often used to create MCT CBD oil where isolate is mixed with a carrier oil such as olive oil or hemp seed oil.
What does Broad Spectrum mean?
CBD Oil that contains a wide range of cannabinoids such as CBG and CBN, but without THC. During the extraction process to remove THC, other cannabinoids can also be lost.
Interested in learning more about full spectrum vs isolate?
In Closing
CBD is still in the early stages of research, therefore anecdotal evidence is heavily relied upon. CBD is still not approved by the FDA, so claims about the benefits are still restricted for non-proven products.
For more information on the effects of the compound cannabidiol, we recommend researching the latest reliable CBD research to find out more.
Always do your own research before you try CBD products, and seek medical advice if you are on medication or have any pre-existing conditions.
Endoca CBD products do not intend to treat, cure, or diagnose any illness, disease, or condition.






